Supporting Smallholder Farmers – What Works and What Doesn’t
Smallholder farmers play a vital role in feeding the world, yet they often face significant challenges in their farming efforts. These challenges range from economic issues such as lack of access to credit and poor access to markets, to limited access to knowledge about best practices. These challenges often make it difficult for smallholder farmers to earn a living and support their families.
What are some of the best practices for supporting smallholder farmers? Who are the stakeholders and what role do they play in supporting the farmers? What approaches have been successful in supporting smallholder farmers and what are the potential pitfalls?
Approaches for Supporting Smallholder Farmers
In order to support smallholder farmers and help them overcome these challenges, a variety of approaches are needed. Some of the best practices for supporting smallholder farmers include access to credit, training and education, and the use of technology. In addition, sustainability and regenerative agriculture also play an important role.
Access to credit. One of the key challenges faced by smallholder farmers is lack of access to credit. Without access to financial resources, it can be difficult for smallholder farmers to invest in the equipment and inputs they need to grow crops and raise livestock. Providing smallholder farmers with access to credit and other financial resources can be an important way to support their efforts and help them overcome this challenge.
Training and Education. In addition to financial support, smallholder farmers also need access to education and training to help them improve their farming practices and increase their yields. This can include training in sustainable farming techniques, such as regenerative agriculture. This approach seeks to restore and improve soil health while minimizing negative environmental impacts.
Technology also plays a significant role in supporting smallholder farmers. New technologies can potentially help them to overcome the above challenges and improve their operations. However, many of these technologies are expensive and may not be accessible to smallholder farmers.
Software-based technologies that can be also accessed through mobile phones may be more accessible to smallholder farmers, as they are often less expensive and more widely available. These technologies may include AI-powered tools such as predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms. Such tools can help smallholder farmers to make more informed decisions about how to manage their farms and predict market demand. For example, apps that provide access to weather data and satellite imagery can help smallholder farmers to better predict weather patterns and plan their operations accordingly.
In addition, new AI-based technologies can potentially help smallholder farmers to predict outbreaks of pests and diseases. They can also recommend the most appropriate pesticides and fertilizers to apply. These technologies may also be able to help smallholder farmers to identify and apply best practices, which can help to improve the sustainability of their operations and increase their yields.
An example of an AI-based technology that can help smallholder farmers is yieldsApp. This platform not only helps farmers make informed decisions, but it also connects smallholder farmers with stakeholders, helping to build resilience in the supply chain. It provides stakeholders with tools that give them transparency and traceability in their supply chain, and enables them to disseminate their knowledge to the farmers.
Sustainability is another key consideration in supporting smallholder farmers. Smallholder farmers can often be at the forefront of sustainable agriculture practices, including regenerative agriculture techniques. These practices can help to improve soil health, reduce erosion, and increase crop yields, while minimizing negative environmental impacts.
However, smallholder farmers may face challenges in transitioning to regenerative agriculture, particularly if they lack the resources or training needed to implement new practices.
Share of global crop production by farm size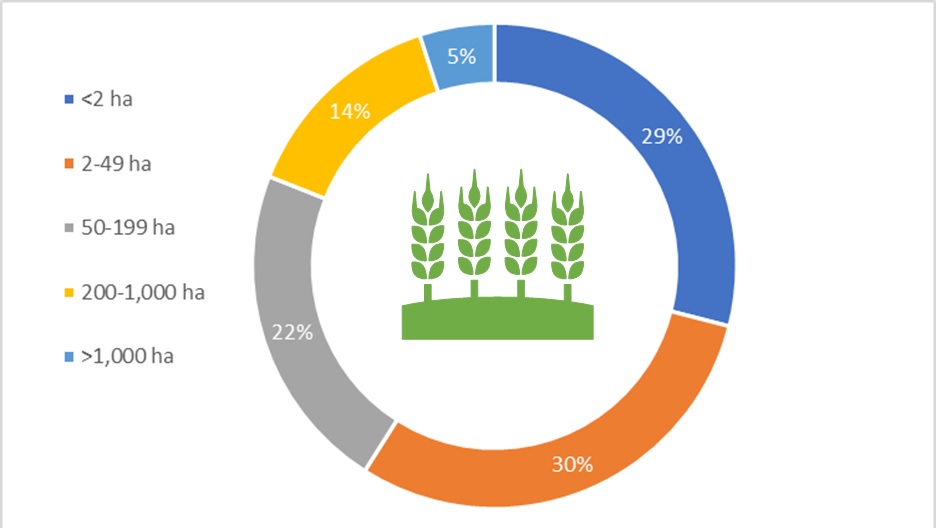
Key Players in Supporting Smallholder Farmers
Governments and NGOs also have an important role to play in supporting smallholder farmers. Governments can support smallholder farmers through policies and initiatives. Such initiatives are aimed at improving smallholder farmers’ access to credit, education and promoting regenerative agriculture by providing training.
NGOs may work directly with smallholder farmers to provide them with access to education, resources, and technologies that can help them to improve their operations and overcome challenges. NGOs may also work with governments, businesses, and other stakeholders to advocate for policies and practices that support smallholder farmers and promote sustainable agriculture.
Food and beverage companies have a significant role to play in supporting smallholder farmers. In addition to establishing fair trade practices and paying fair prices for agricultural products, these companies can also support smallholder farmers through education and knowledge transfer. Many food and beverage companies have programs in place to educate smallholder farmers about best practices for growing crops and raising livestock, as well as providing them with access to resources such as seedlings, fertilizers, and equipment.
By transferring knowledge and providing smallholder farmers with the tools, access to technology, and resources they need to succeed, food and beverage companies can help to improve the lives of smallholder farmers and increase the sustainability of their operations.
This is not only beneficial for smallholder farmers, but it is also in the interest of food and beverage companies, as it helps to ensure a stable and sustainable supply chain for their products.
In addition, supporting smallholder farmers can also help food and beverage companies to achieve their net zero targets.
As climate change continues to be a major global challenge, more and more companies are setting ambitious net zero targets in an effort to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate their impact on the environment. One way that food and beverage companies can help to achieve these targets is by supporting smallholder farmers in their efforts to adopt sustainable agriculture practices.
By providing smallholder farmers with access to education, resources, and technologies that can help them to grow crops and raise livestock in a more sustainable way, food and beverage companies can help to reduce the environmental impact of their supply chain and contribute to their net zero goals.
Challenges and Pitfalls in Supporting Smallholder Farmers
The above approaches seem to be effective in helping smallholder farmers overcome challenges and succeed. However, it’s also important to consider what doesn’t work, in order to better understand how to address the unique challenges faced by smallholder farmers.
Single aspect approach. An approach that may not be effective is focusing solely on one aspect of smallholder farming, such as improving access to credit or increasing crop yields, without addressing the broader context in which smallholder farmers operate. Smallholder farmers often face a complex array of challenges, and addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach that takes into account the many different factors that impact their success.
Handouts. One approach that may not be effective in supporting smallholder farmers is providing them with financial aid or handouts. While it’s true that smallholder farmers often lack access to credit and other financial resources, simply providing them with money may not be the most effective way to support their efforts. This is because smallholder farmers also need access to education, training, and other resources in order to improve their farming practices and increase their yields.
Inappropriate technologies. Providing smallholder farmers with technologies or inputs that are not appropriate for their specific needs or context: It’s important to carefully consider the needs and capabilities of smallholder farmers before providing them with technologies or inputs. If these technologies or inputs are not appropriate for the specific needs or context of the smallholder farmer, they may not be effective in helping them overcome challenges and succeed.
Ignoring cultural context. Neglecting to consider the social and cultural context in which smallholder farmers operate: Smallholder farmers often operate within specific social and cultural contexts that can impact their ability to adopt new technologies or practices. It’s important to consider these contextual factors when developing strategies for supporting smallholder farmers.
Lack of farmer involvement. Failing to involve smallholder farmers in the planning and implementation process: Smallholder farmers are the experts when it comes to their own operations and challenges. It’s important to involve them in the planning and implementation process in order to ensure that any support or assistance provided is appropriate and effective.
Ignoring unintended consequences. Not considering the potential unintended consequences of support or assistance: Any support or assistance provided to smallholder farmers should be carefully designed to minimize the potential for unintended consequences. For example, providing smallholder farmers with subsidies or other financial incentives may alter their decision-making and potentially have unintended consequences on their long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s important to carefully consider the needs and capabilities of smallholder farmers and the specific context in which they operate when developing strategies for supporting them. Failing to consider these factors or neglecting to involve smallholder farmers in the planning and implementation process, may result in approaches that are not effective in helping smallholder farmers overcome challenges and succeed.


