Embracing the Future of Precision Agriculture: Overcoming Challenges and Setting Future Goals
Precision agriculture has transformed farming practices by integrating advanced technologies to optimize crop production and resource management. While the benefits of precision farming are evident, many growers and agronomists face significant challenges. Understanding these challenges and setting future goals are crucial for maximizing the potential of precision agriculture.
Challenges in Precision Agriculture
Data Management Complexity
One of the primary challenges in precision agriculture is managing the diverse data generated by various technologies. Growers often find themselves dealing with multiple file types from different equipment manufacturers, such as Case IH, Ag Leader, AGCO, Trimble, Precision Planting, and Kuhn. This diversity complicates data analysis and management, requiring significant time and effort to convert and integrate data from different sources.
The goal for many is to streamline data management by reducing the number of file types they need to handle. Consolidating data formats can simplify the process, making it easier to analyze and use the information to make informed decisions. Moving towards a more unified data management system will enhance efficiency and reduce the burden on growers and agronomists.
Adoption of New Technologies
While precision agriculture technologies like auto-guidance and row shutoff have seen widespread adoption, other tools such as variable rate technology (VRT) have been slower to gain traction. This slow adoption rate can be attributed to various factors, including cost, complexity, and the need for specialized knowledge.
Growers need to carefully evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of new technologies. Investing in technologies that provide the most significant return on investment is essential. However, the initial costs and learning curve associated with new technologies can be a deterrent for many. Support from agricultural extension services and technology providers in training and education can help bridge this gap.
Data Privacy and Sharing Concerns
Another challenge is the reluctance to share data. Many growers are hesitant to share their data due to privacy concerns and fear of misuse. This reluctance can hinder collaborative efforts and limit the potential benefits of shared data analysis. Building trust and ensuring data privacy and security are crucial for encouraging growers to participate in data-sharing initiatives.
Soil and Water Management
Effective soil and water management are critical components of precision agriculture. However, optimizing irrigation can be challenging, especially in regions with variable soil types and climatic conditions. Managing surface drainage, preventing waterlogging, and ensuring efficient water distribution require advanced technologies and precise strategies. Soil testing remains a cornerstone of precision agriculture, but the traditional methods of soil sampling and lab analysis can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. There is a growing need for more efficient and on-the-go soil testing methods that can provide real-time data for informed decision-making.
Technical Support and Maintenance
Accessing reliable technical support and regular maintenance for precision agriculture technologies is crucial for their effective use. Farmers often face challenges in keeping sophisticated equipment and software functioning optimally. Ensuring that there is readily available support to address technical issues and perform routine maintenance can minimize downtime and maximize productivity. Collaborating with technology providers to establish robust support networks can help farmers maintain their precision agriculture systems efficiently.
Data Interpretation Skills
The need for advanced skills to interpret complex data accurately and make informed decisions is another significant challenge in precision agriculture. With the vast amounts of data generated by various technologies, farmers must have the expertise to analyze and understand this information. Developing these skills requires comprehensive training and education.
Future Goals in Precision Agriculture
Streamlined Data Management Systems
The future of precision agriculture lies in developing streamlined data management systems that can handle diverse data formats seamlessly. Integrating data from various sources into a unified platform will enable growers to analyze and use data more efficiently. Advancements in cloud-based storage solutions and data management software will play a pivotal role in achieving this goal.
 Precision agriculture technology
Precision agriculture technology
Enhanced Adoption of Precision Technologies
Increasing the adoption rate of precision technologies like VRT requires a concerted effort from technology providers, researchers, and extension services. Providing comprehensive training and support can help growers understand the benefits and applications of these technologies. Demonstrating the tangible benefits through case studies and pilot projects can also encourage wider adoption.
Advanced Soil and Water Management Solutions
Developing advanced soil and water management solutions is crucial for addressing the challenges of excess water and nutrient management. On-the-go soil testing technologies that provide real-time data will revolutionize soil management practices. Additionally, integrating precision irrigation systems with real-time monitoring can optimize water use and improve crop yields.
Data Privacy and Collaborative Efforts
Building a culture of trust and collaboration is essential for the future of precision agriculture. Establishing robust data privacy policies and secure data-sharing platforms can alleviate growers’ concerns about data misuse. Collaborative efforts among growers, agronomists, researchers, and technology providers can lead to innovative solutions and improved agricultural practices.
The path forward in precision agriculture requires addressing key challenges and leveraging innovative solutions. Managing data complexity, adopting new technologies, ensuring data privacy, and improving technical support and data interpretation skills are critical steps. By focusing on streamlined data management systems, enhancing the adoption of precision technologies, and fostering a culture of trust and collaboration, growers and agronomists can overcome these challenges. Embracing comprehensive and integrated systems will streamline data, improve efficiency, and promote sustainability, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable agricultural future.
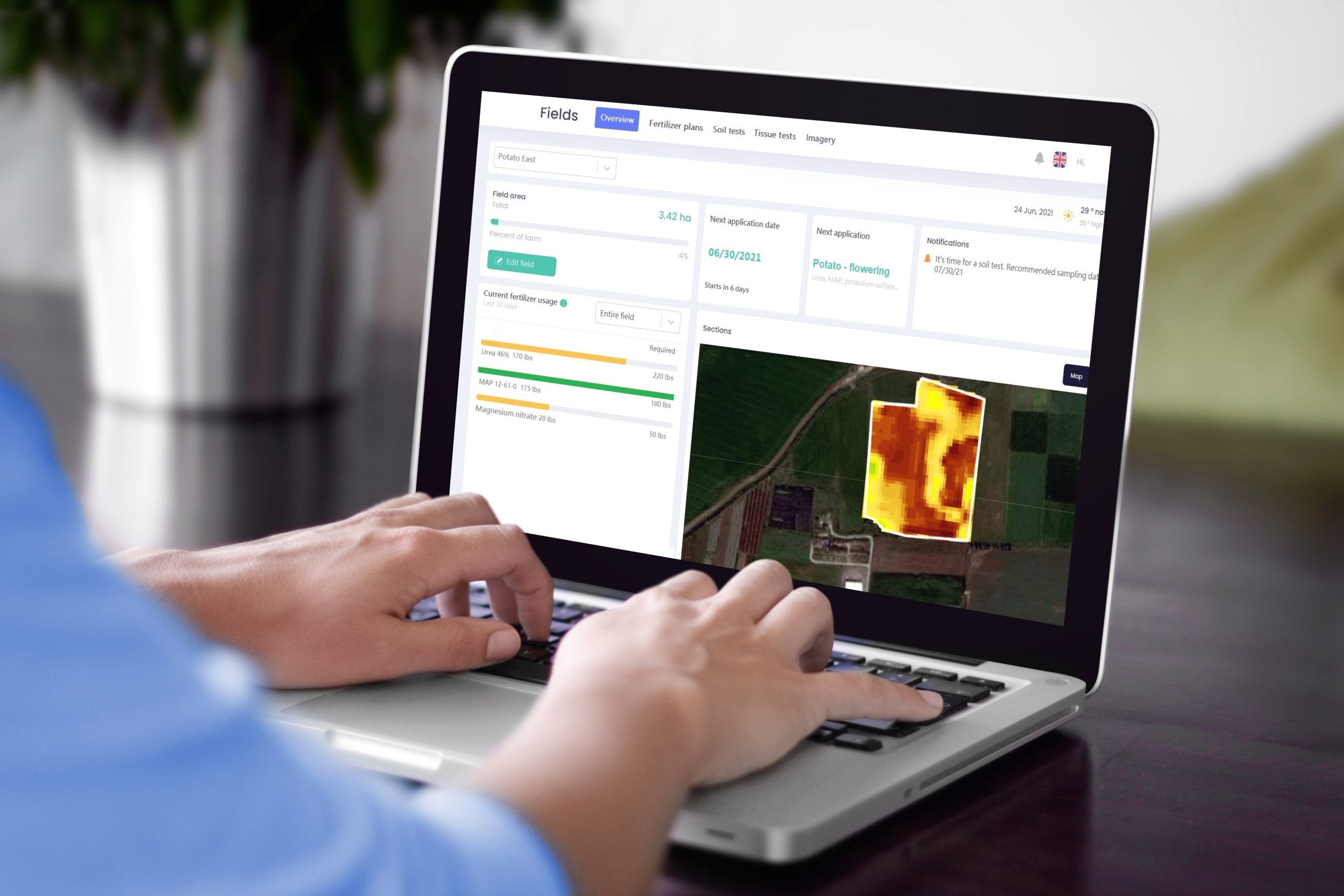
yieldsApp, for example, is one of the players in the market that plays a significant role in this transformation by providing comprehensive data management and analysis tools. It generates dynamic crop management protocols such as fertilizer plans, pest and disease treatment plans and irrigation scheduling. As an “all-in-one” system, yieldsApp encompasses all agronomic practices along with essential farm management features. This streamlines data and avoids the need to use multiple applications, making it easier for growers to maximize their productivity and sustainability, paving the way for a more efficient and prosperous agricultural future.



