Hydroponic systems
Hydroponics is a growing method in which plants are grown in a mineral nutrient solution, with or without the use of a growing medium. There are several types of hydroponic systems, which will be further described.
Growing in hydroponics is gaining popularity, as it has many advantages:
- Uses less space
- Saves water, as water is recirculated or can be reused
- There are no weeds
- Plant environment is controlled
- There are no constrains related to soil, such as pH and salinity
- Reduced plant diseases
On the other hand, growing in hydroponics also has some disadvantages:
- It requires deeper knowledge
- There is less room for errors
- Once occurred, diseases can spread quickly
- The initial costs are high
Materials that are commonly used as growing media include perlite, peat, coco peat, volcanic ash, montmorillonite, rockwool etc.
The main purpose for using a growing medium is to provide support for plant roots. Growing media do not retain much nutrients and many are inert materials and do not retain nutrients at all. The nutrient solution is, therefore, the main source of nutrients for plants grown in hydroponics. It consists of water and mineral nutrient, which are added with dissolved fertilizers.
In several hydroponic system types, the nutrient solution can be recirculated and re-used.
Types of hydroponic systems
Hydroponics systems can have different designs and use different methods. The main system types are:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
- Deep water culture
- Ebb and flow
- Wick systems
- Hydroponic drip systems
- Aeroponics
Nutrient film technique (NFT) – in this method, plant roots are exposed to a continuous flow of a nutrient solution film. Plants are placed in planting holes along channels, where the channels are placed at an angle that allows water to flow by gravity towards a drain pipe. The thin film of nutrient solution is continuously recirculated.
NFT system
Deep water culture – Plant roots are placed directly in a nutrient solution. Oxygen is injected to the water.
Deep water culture
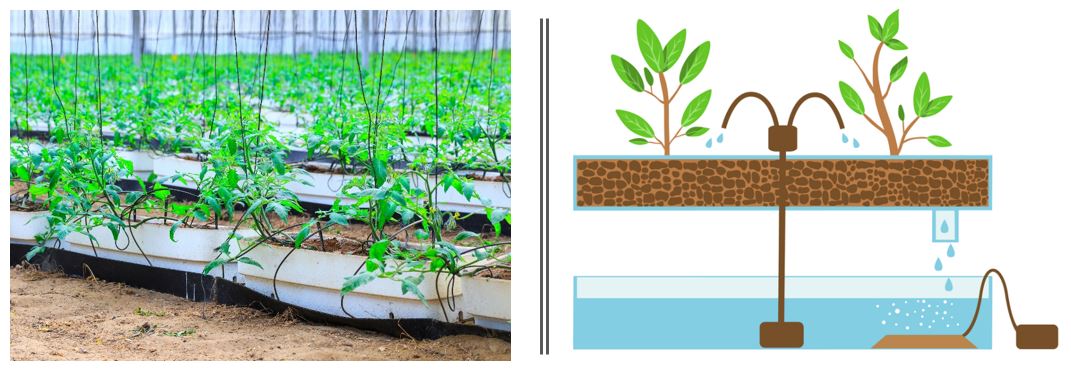
Ebb and flow – Potted plants are placed in a growing tray. The tray is flooded with a nutrient solution, until it reaches a certain level. Then, the water drains and can be reused.
Wick system – A passive hydroponic system in which one side of fibrous nylon ropes are placed around the plants, in the growing medium, while their other side is placed in the nutrient solution reservoir. The nutrient solution goes up the wicks to the plants by capillary action.
Drip irrigation– In these systems, the nutrient solution is delivered to the plants by a drip system. The plants are placed containers such as bags, pots, slabs, beds etc. The drainage coming out from the bottom of the container can be recirculated.
Drip irrigation system
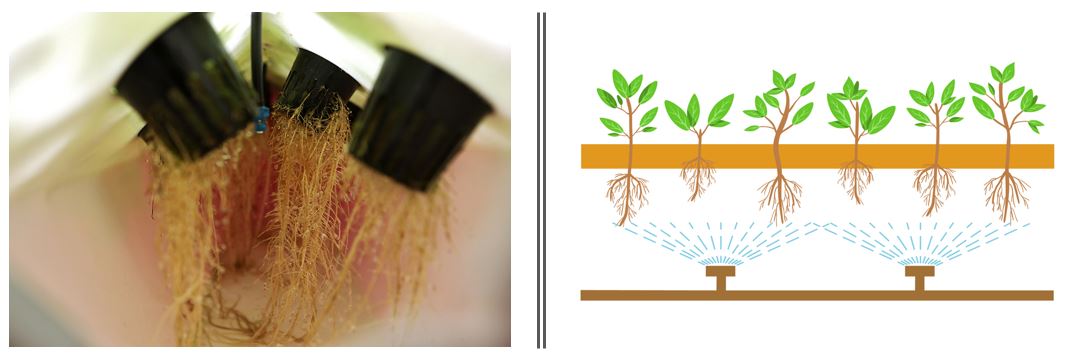
Aeroponics – Plant roots are suspended in air, while nozzles spray the nutrient solution directly on the roots at certain intervals.
Aeroponic system